Hypokalæmia: Long QTc or QU
Report:
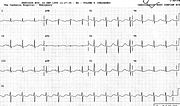
Sinus rhythm 87/min
Diffuse ST/T changes
Long QT interval 0.48”
QTc 0.50”
Comment
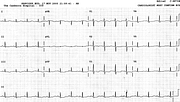
It is practically impossible to tell QT from QU here. The patient was known, however, to have potassium 1.9 mEq/L, with normal calcium and magnesium. Accordingly, what we are looking at is a TU morphology, probably of the same significance as true QT prolongation33. Abnormalities improved but persisted day after potassium was normalised (23a).
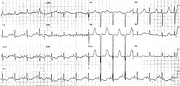
In Fig 23b is another patient, a 34 year old alcoholic, with vomiting-induced hypokalæmia (2.0 mEq/L) and alkalosis. He in fact arrested in VF in Casualty. The reason for his prominent P waves is unknown; hypokalæmia, even marked, usually causes only a modest increase in P wave amplitude. His U waves were quite tall; at times hyperkalæmia is suspected by the uninitiated.
If you have any suggestions for or feedback on this report, please let us know.
Hi, can we chat about some terms and conditions?
The library and it's records are licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International license.
You are free to:
- Share — copy and redistribute the material in any medium or format for any purpose, even commercially.
- Adapt — remix, transform, and build upon the material for any purpose, even commercially.
- The licensor cannot revoke these freedoms as long as you follow the license terms.
Under the following terms:
- Attribution — You must give appropriate credit , provide a link to the license, and indicate if changes were made . You may do so in any reasonable manner, but not in any way that suggests the licensor endorses you or your use.
- No additional restrictions — You may not apply legal terms or technological measures that legally restrict others from doing anything the license permits.
By clicking agree below, you are agreeing to adhere to CC BY 4.0.